Introduction
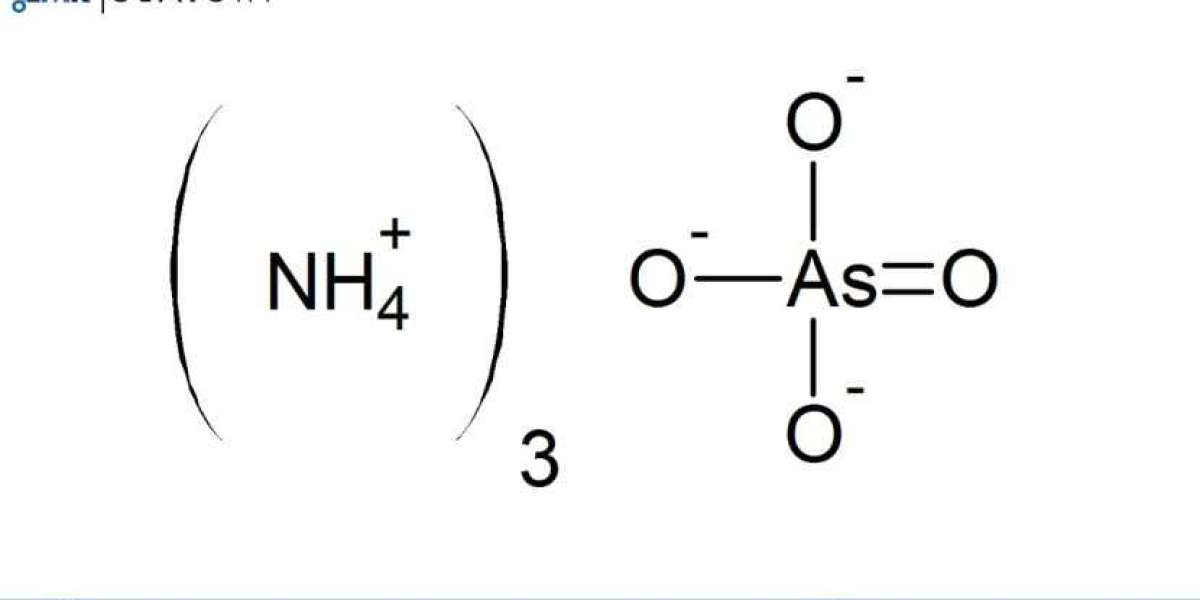
An Ammonium Arsenite Manufacturing Plant Project Report is a detailed guide that outlines the necessary steps, processes, equipment, financial considerations, and regulatory requirements for setting up a plant to produce Ammonium Arsenite. Ammonium Arsenite is an important inorganic compound used primarily in pesticides, herbicides, and other industrial applications. Due to its significant role in agriculture, Ammonium Arsenite is widely used for controlling pests, particularly in the management of fungal diseases in crops.
This project report is essential for entrepreneurs, investors, and manufacturers who are looking to set up a production facility for Ammonium Arsenite. It provides a comprehensive overview of everything required, from raw materials and production processes to market analysis and regulatory compliance, to ensure the establishment of a successful and compliant manufacturing plant.
Industry Overview
The demand for Ammonium Arsenite is primarily driven by its use as a pesticide and fungicide in agriculture. The global agrochemical market has been expanding rapidly due to the increasing need for food production and the growing population. Pesticides and herbicides play an essential role in protecting crops from diseases, pests, and weeds. As agriculture continues to grow, particularly in emerging economies, the demand for chemical pesticides, including Ammonium Arsenite, is expected to rise.
However, there are challenges related to the use of arsenic compounds, as arsenic is toxic and poses environmental risks. As such, the production and sale of Ammonium Arsenite are subject to strict regulations and safety standards. The growth of organic farming and the shift toward more sustainable agriculture practices has also led to a gradual decline in the use of traditional chemical pesticides. Nevertheless, Ammonium Arsenite remains a key ingredient in various agricultural solutions due to its effectiveness.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Raw Materials for Ammonium Arsenite Production
The production of Ammonium Arsenite involves the use of several raw materials, each of which must be carefully sourced and handled due to their chemical properties and potential hazards. The key raw materials are:
1. Arsenic Trioxide (As2O3)
- Arsenic Trioxide is the primary raw material used in the production of Ammonium Arsenite. It is an inorganic compound that serves as a source of arsenic in the final product. Arsenic Trioxide is typically produced by heating arsenic-containing ores or refining copper and other metals.
2. Ammonium Hydroxide (NH4OH)
- Ammonium Hydroxide is used to neutralize the arsenic trioxide, reacting with it to form Ammonium Arsenite. It is a strong base, and its concentration must be controlled to ensure the proper formation of the compound.
3. Water
- Water is used to dissolve both arsenic trioxide and ammonium hydroxide during the production process. Water also plays a role in washing away impurities and controlling the temperature of the reaction.
4. Other Chemicals
- Stabilizers and precipitants may be used to control the purity and consistency of the final product. Additionally, other additives could be employed to adjust the physical properties of the product for specific applications.
Manufacturing Process
The production of Ammonium Arsenite involves several critical steps, including the preparation of raw materials, chemical reaction, precipitation, filtration, and drying. Below is a detailed description of each stage of the manufacturing process:
1. Preparation of Raw Materials
- The first step in the process involves preparing the raw materials. Arsenic Trioxide is typically in a powdered form, and Ammonium Hydroxide is available as a concentrated aqueous solution. Both materials are handled with extreme caution due to their toxic and reactive nature.
2. Chemical Reaction
- In a reaction vessel, Arsenic Trioxide is dissolved in water, and Ammonium Hydroxide is gradually added to the solution. The solution formed is a suspension of Ammonium Arsenite in water. It is important to control the reaction temperature and the concentration of ammonium hydroxide to ensure that the desired product is formed.
3. Precipitation and Filtration
- After the reaction is complete, the Ammonium Arsenite precipitates from the solution. This solid is then separated from the liquid using filtration. Filtration ensures that the final product is free from any unreacted raw materials or impurities.
4. Washing and Purification
- The precipitate is washed with water to remove any residual chemicals or by-products. This washing process is essential to ensure that the final product has a high level of purity, which is crucial for its effectiveness in agricultural applications.
5. Drying
- After washing, the Ammonium Arsenite is dried to remove excess moisture. The drying process is typically done using low-heat drying techniques to avoid decomposition or loss of product during the drying phase.
6. Grinding and Sifting
- Once dried, the Ammonium Arsenite may be ground into a fine powder for easier handling, packaging, and application. It may also be sifted to ensure uniform particle size.
7. Packaging
- The final Ammonium Arsenite product is packaged in appropriate containers, such as sealed plastic bags, drums, or other packaging solutions designed to prevent contamination and ensure safe handling. The product is labeled according to industry standards and regulatory requirements, including safety warnings and usage instructions.
Plant Setup and Infrastructure
Establishing a manufacturing plant for Ammonium Arsenite requires careful planning and consideration of infrastructure, machinery, safety measures, and environmental regulations. The following are key aspects to consider:
1. Location
- The plant should be located in an industrial zone with good access to raw material suppliers and transportation routes. Proximity to a water source is essential for the chemical reaction and cooling purposes.
2. Factory Layout
- The factory layout should ensure the safe handling of raw materials and chemicals. Key areas of the plant include:
- Raw Material Storage: For storing arsenic trioxide, ammonium hydroxide, and other chemicals in secure, temperature-controlled environments.
- Reaction Area: Where the chemical reaction occurs in controlled reactors or vessels.
- Filtration and Purification Area: For separating and purifying Ammonium Arsenite.
- Drying and Packaging Area: For drying, grinding, and packaging the final product.
- Safety and Waste Management Area: For handling toxic chemicals and waste materials.
3. Machinery and Equipment
- Essential machinery and equipment include:
- Reaction Vessels: For dissolving arsenic trioxide and reacting it with ammonium hydroxide.
- Filtration Units: For separating the solid Ammonium Arsenite from the liquid.
- Dryers: To dry the Ammonium Arsenite after purification.
- Grinders and Sieves: For processing the product into the desired consistency.
- Packaging Equipment: For packing the final product into containers for distribution.
4. Utilities
- The plant will require a consistent supply of electricity, water, and steam for the chemical reactions and operational processes. Adequate ventilation and safety equipment must be in place to manage any toxic fumes or hazards associated with arsenic-based chemicals.
5. Safety Measures
- Given the toxicity of the chemicals involved, safety measures must be strictly followed:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers must wear appropriate PPE such as gloves, goggles, and protective clothing.
- Emergency Systems: Emergency showers, eyewash stations, and fire suppression systems should be available.
- Waste Disposal: Proper systems for the disposal of hazardous waste and by-products must be established.
Cost Analysis and Financial Planning
Setting up an Ammonium Arsenite manufacturing plant involves considerable capital investment and operational costs. The major components of the cost structure include:
1. Capital Investment
- Land and Infrastructure: The cost of purchasing or leasing land, constructing the plant, and installing essential utilities.
- Machinery and Equipment: Investment in reaction vessels, filtration systems, dryers, grinders, and packaging machines.
- Raw Materials: Initial purchase of arsenic trioxide, ammonium hydroxide, and other necessary chemicals.
2. Operational Costs
- Labor Costs: Wages for production workers, engineers, quality control staff, and administrative personnel.
- Raw Materials: Ongoing procurement of arsenic trioxide, ammonium hydroxide, and other chemicals.
- Utility Costs: Expenses for water, electricity, and waste management.
3. Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
- The plant must comply with local, national, and international regulatory standards. Costs associated with safety, environmental impact assessments, and product certifications must be factored into the budget.
4. Marketing and Distribution
- Marketing: A budget for advertising and promoting Ammonium Arsenite in target markets, especially agricultural sectors.
- Transportation: Costs for logistics and distribution to local and international markets.
5. Profitability and Return on Investment (ROI)
- The profitability of the plant depends on efficient production processes, maintaining product quality, and meeting market demand. With a growing global demand for pesticides and herbicides, the Ammonium Arsenite market is expected to be lucrative.
Regulatory Considerations
The production of Ammonium Arsenite is regulated due to its toxic and hazardous nature. Key regulations to consider include:
- Environmental Regulations: To minimize the environmental impact of arsenic and chemical waste.
- Occupational Health and Safety Standards: To ensure the safety of workers in the manufacturing plant.
- Agricultural and Pesticide Regulations: Compliance with agricultural regulations for the use of Ammonium Arsenite in pesticides.